11.4 Models Overview
Starting point for the Bayesian models were to relax some of the assumptions of the Mack method:
LCL: Relaxes the first assumption where Mack treats loss to date as a fixed level parameters
CCL: Builds on top of LCL and allows for AY correlations, which relaxes the 2nd assumption of Mack
Prior distributions
Paper uses diffuse prior for the most part since the author doesn’t have direct knowledge of the business
Given more direct knowledge of the underlying business, we can specify more restrictive priors for \(\{\alpha_w\}\) and \(logelr\)
Bayesian Models:
Leveled Chain-Ladder (LCL): Add variability to the row parameter
Correlated Chain-Ladder (CCL): Add AY correlation \(\rho\)
Leveled Incremental Trend (LIT): Use skewed distribution and CY trend \(\tau\)
Correlated Incremental Trend (CIT): LIT with added AY correlation \(\rho\)
Changing Settlement Rate (CSR): LCL with speed up claims closure \(\gamma\)
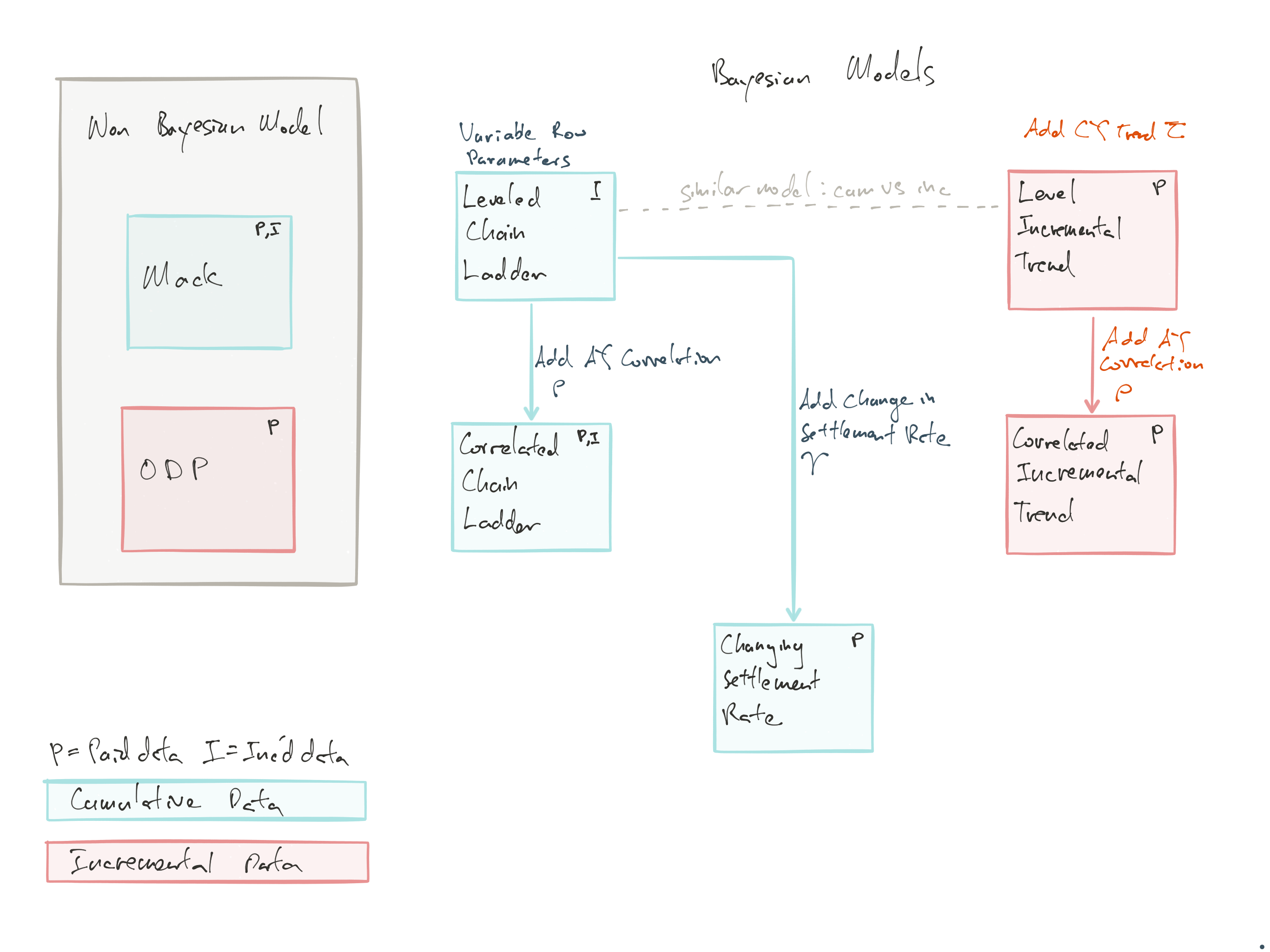
Figure 11.3: Overview of models
Non-Bayesian Models:
England & Verall ODP: See Shapland, but doesn’t have the residual adjustments
Remark. Non-Bayesian Models
Mack is the only one that does not have a base form of \(\mu_{wd} = \alpha_w + \beta_d\)
- ODP is the England & Verall Bootstrap